IncidentResponsev2
4.09 Install and Deploy Security Onion
Task
Install and Deploy Security Onion
Conditions
Given a Linux Security Onion machine.
Standards
- Configuring Security Onion (SO) from an instantiated virtual machine.
- Setup Security Onion firewall rules.
- Connecting to Security Onion from another box for log visibility and analyst access.
End State
Fully functioning Security Onion NIDS receiving and parsing logs from target network segments.
Manual Steps
Configuring Security Onion from an instantiated virtual machine
- Login to SO.
Note: for lab/range use credentials from SharePoint.
-
Open Terminal → Click
Applications→Utilities→Terminal. Leave terminal off to the side. - Launch setup → Double click setup icon on desktop.
Note: Use password from Step 1.1 in setup.
-
Select
Yes, Continue! -
Select
Yes, configure /etc/... - Select the management interface:
- In Terminal type
ip address - Verify the interface IPv4 address matches what is selected.
- In Terminal type
-
Set a static IP → Make sure static is selected → Select
Ok. -
Input IPv4 address → select
Ok→ refer to Terminal output. -
Input your subnet CIDR → select
Ok. - Input your gateway:
ip route -
Use IP after
default viafor gateway. - Input your DNS → In Terminal:
nslookup google.com -
Use displayed DNS servers.
- Input your domain name:
hostname -f -
Input everything after first period → select
Ok. -
Configure sniffing interfaces → select
Yes, configure... -
Ensure management interface is NOT selected → select
Ok. -
Select
Yes, make changes! -
Select
Yes, Reboot! -
Login to SO again → Use original credentials.
-
Launch setup again → double click setup icon.
-
Input system logon password.
-
Select
Yes, Continueto configure services. -
Select
Yes, skip...to skip prior config. -
Select
Production Mode. -
Select
Newdeployment. -
Input first user account (not default) → set password twice.
-
Select
Best Practices. -
Select
Emerging Threats Openruleset. -
Select
SnortIDS engine. -
Select
Enable our sensors. -
Accept default port configurations → Select
Ok. -
Review monitoring interfaces → confirm management interface NOT selected → Select
Ok. -
Define HOME_NET subnets → Input each subnet in CIDR → comma separated.
-
Store logs locally → Select
Yes. -
Accept default log size → Select
Ok. -
Finish configuration → Select
Yes, proceed... - Confirm and accept defaults until complete → Select
Oksix times.
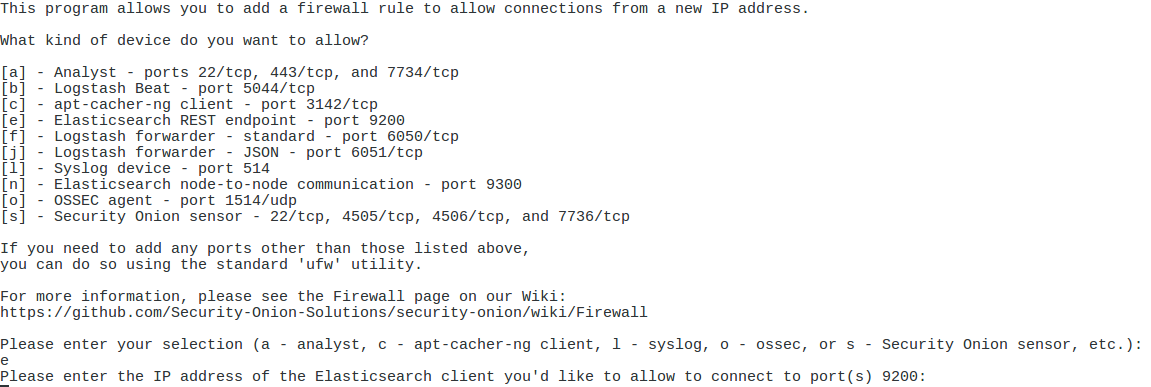
Setup Security Onion Firewall Rules (so-allow)
After initial setup, configure local firewall to permit necessary communications.
- Open Terminal:
sudo so-allow
Allow analyst access
Allows workstations or ranges to access SO web interfaces.
sudo so-allow
Allow Elasticsearch access
Allows other SO boxes or apps to connect to Elasticsearch.
sudo so-allow
Allow PAN syslog device
Allows Palo Alto to forward logs to SO.
sudo so-allow
Allow Wazuh/OSSEC agent connectivity
Allows workstations/servers running Wazuh agent to report into SO.
sudo so-allow
Operator Note: Always validate and limit scope → use DAPE (Deny All, Permit by Exception) logic.
Connecting to Security Onion from Another Box
- On analyst laptop:
- Open web browser.
- Enter IP of Security Onion management interface.
- If connection fails:
- Validate analyst workstation is in same subnet.
- Check firewall rules:
sudo ufw status numbered sudo ufw delete <rule_number>
- Once connected → Open Kibana from web interface.
- Login using credentials created in step 1.15.
Operator Note: This step validates operational readiness → Kibana access confirms sensors and ingestion are online.
Dependencies
- Security Onion virtual machine.
- Network access and static IP configuration.
- Proper subnet and CIDR information.
- Access to Security Onion and analyst workstations.
Other Available Tools
| Tool | Platform | Installation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| so-allow | Security Onion | Built-in | Configures firewall access rules |
| Kibana | Web UI | Built-in | Visualize and search logs |
| ElasticSearch | Backend | Built-in | Stores log data |
Operator Recommendations and Additional Tools
Operator Checklist
- Install and configure Security Onion from virtual machine.
- Assign static IP, gateway, subnet, DNS, and domain during setup.
- Complete production mode configuration and sensor setup.
- Configure firewall rules via
so-allowfor analyst, PAN, Wazuh, and OSSEC agents. - Validate remote analyst access to SO web interface.
- Verify Kibana log visibility for HOME_NET.
Best Practices
- Use
so-allowcautiously → opening too much access weakens NIDS. - Verify all subnets and IP ranges carefully → especially HOME_NET.
- Regularly test Kibana and sensor ingestion after deployment.
- Create snapshot or backup after successful install for quick redeployment.
References
Security Onion Docs
Security Onion Docs - Local
Security Onion Walkthrough
Revision History
| Date | Version | Description | Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-05-02 | 1.0 | Final corrected version preserving original + expanded operator instructions, validation, and context | Leo |